Solid carbide deburring tool, 60° DIN 6527, HB shank
Milling cutter SC DIN6527 Z4-6 60° type N TiAlN HB
DEBURTL-DIN6527-60DGR-SC-TN-D6MM
Art.-no. 5443301532
EAN 4055375923511
Individual price display after login












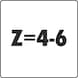


Exclusively for trade customers
Register now and access more than 125,000 products
Universal range of applications, particularly suitable for chamfering and deburring and for contouring.
Product information
Datasheets(X)
 | |
Product code | 7727 |
Material to be processed | Steel, Cast metal, Stainless steel, Aluminium |
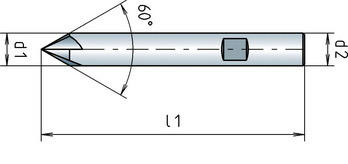
Diameter (d1) | 6 mm |
Shank diameter (d2) | 6 mm |
Standards | DIN 6527 |
Shank style | Cylindrical DIN 6535-HB |
Cutting material | SC |
Surface | TiAlN |
Length (l1) | 57 mm |
Number of cutting edges (Z) | 4 PCS |
Angle of the tip | 60 Degree |
Tolerance of cutting edge diameter | h10 |
Tolerance of shank diameter | h6 |
Material of sub-group | General structural steels, Non-alloyed tempering steels < 1000 N/mm², Alloyed tempering steels < 1000 N/mm², Nitriding steels < 1300 N/mm², Grey cast iron, Malleable cast iron, Stainless steels < 850 N/mm², Stainless steels > 850 N/mm², Aluminium |
| Cutting values | ||||||||
| For dia. 4-16 | ||||||||
| Material designation | Tensile strength | Cooling | vc | fz | ||||
| Dia. 4-5.9 | Dia. 6-7.9 | Dia. 8-9.9 | Dia. 10-11.9 | Dia. 12-16 | ||||
| Steels | ||||||||
| General structural steels | < 500 N/mm² | E | 190 | 0,042 | 0,070 | 0,082 | 0,094 | 0,104 |
| 500-850 N/mm² | E | 170 | 0,042 | 0,070 | 0,082 | 0,094 | 0,104 | |
| Carbon steels | < 850 N/mm² | E | 170 | 0,042 | 0,070 | 0,082 | 0,094 | 0,104 |
| 850-1000 N/mm² | E | 140 | 0,030 | 0,047 | 0,059 | 0,070 | 0,082 | |
| Unalloyed heat-treated steels | < 700 N/mm² | E | 170 | 0,042 | 0,070 | 0,082 | 0,094 | 0,104 |
| 700-850 N/mm² | E | 160 | 0,042 | 0,070 | 0,082 | 0,094 | 0,104 | |
| 850-1000 N/mm² | E | 140 | 0,030 | 0,047 | 0,059 | 0,070 | 0,008 | |
| Alloyed heat-treated steels | 850-1000 N/mm² | E | 120 | 0,030 | 0,047 | 0,059 | 0,070 | 0,008 |
| 1000-1200 N/mm² | E | 95 | 0,026 | 0,039 | 0,052 | 0,065 | 0,078 | |
| Unalloyed case-hardening steels | < 750 N/mm² | E | 170 | 0,042 | 0,070 | 0,082 | 0,094 | 0,104 |
| Alloyed case-hardening steels | < 1000 N/mm² | E | 120 | 0,030 | 0,047 | 0,059 | 0,070 | 0,082 |
| 1000-1200 N/mm² | E | 95 | 0,026 | 0,039 | 0,052 | 0,065 | 0,078 | |
| Nitriding steels | < 1000 N/mm² | E | 120 | 0,030 | 0,047 | 0,059 | 0,070 | 0,082 |
| 1000-1200 N/mm² | E | 95 | 0,026 | 0,039 | 0,052 | 0,065 | 0,078 | |
| Tool steels | < 850 N/mm² | E | 120 | 0,030 | 0,047 | 0,059 | 0,070 | 0,082 |
| 850-1100 N/mm² | E | 95 | 0,026 | 0,039 | 0,052 | 0,065 | 0,078 | |
| 1100-1300 N/mm² | E | 85 | 0,026 | 0,039 | 0,052 | 0,065 | 0,078 | |
| High-speed steels | 850-1200 N/mm² | E | 80 | 0,026 | 0,039 | 0,052 | 0,065 | 0,078 |
| Wear-resistant constructional steel | 1300 N/mm² | E | 50 | 0,008 | 0,033 | 0,042 | 0,039 | 0,070 |
| Spring steels | < 1200 N/mm² | E | 85 | 0,026 | 0,039 | 0,052 | 0,065 | 0,078 |
| Stainless steels | ||||||||
| Stainless steels, sulphurated | < 700 N/mm² | E | 110 | 0,030 | 0,047 | 0,059 | 0,070 | 0,082 |
| Stainless steels, austenitic | < 700 N/mm² | E | 110 | 0,030 | 0,047 | 0,059 | 0,070 | 0,082 |
| < 850 N/mm² | E | 90 | 0,026 | 0,039 | 0,052 | 0,065 | 0,078 | |
| Stainless steels, martensitic | < 1100 N/mm² | E | 75 | 0,026 | 0,039 | 0,052 | 0,065 | 0,078 |
| Special alloys | < 1200 N/mm² | E | 50 | 0,008 | 0,026 | 0,042 | 0,039 | 0,070 |
| Cast metals | ||||||||
| Cast iron | < 180 HB | - | 150 | 0,026 | 0,035 | 0,070 | 0,094 | 0,116 |
| > 180 HB | - | 120 | 0,026 | 0,035 | 0,070 | 0,094 | 0,116 | |
| Nodular graphite, malleable iron | > 180 HB | - | 100 | 0,026 | 0,035 | 0,070 | 0,094 | 0,116 |
| > 260 HB | E | 90 | 0,026 | 0,035 | 0,070 | 0,094 | 0,116 | |
| Graphite | - | - | 150 | 0,026 | 0,035 | 0,070 | 0,094 | 0,116 |
| Non-ferrous metals | ||||||||
| Aluminium, aluminium alloys | < 530 N/mm² | E | 800 | 0,031 | 0,040 | 0,061 | 0,082 | 0,103 |
| Aluminium, cast aluminium alloys < 10 % Si | < 600 N/mm² | E | 600 | 0,031 | 0,040 | 0,061 | 0,082 | 0,103 |
| Aluminium, cast aluminium alloys > 10 % Si | < 600 N/mm² | E | 400 | 0,031 | 0,040 | 0,061 | 0,082 | 0,103 |
| Magnesium, magnesium alloys | < 280 N/mm² | E | 800 | 0,031 | 0,040 | 0,061 | 0,082 | 0,103 |
| Legend |
| E = emulsion |
| vc = cutting speed [m/min] |
| fz = feed per tooth [mm/t] |
| The suggested cutting values are reference values and must be adapted to the respective conditions. |